Learning
new languages is a natural instinct for children, and yet it becomes
more difficult as we age. We might be at a disadvantage as adults, but
with a few learning methods, you can still give yourself the best chance
for learning a new language.
I've been
attempting to learn French for a while now, and it's a slow process.
It's all much harder this time around than it was to learn English, my
first language. All this effort made me wonder if there were some tricks
to learning a foreign language that I'd been missing. It turns out,
it's just a tricky thing to do once you're an adult.
How We Learn Language

Learning language is something we're born to do. it's an instinct we have, which is proven, as one research paper says, just by observation:
To believe that special biological adaptations are a requirement, it is enough to notice that all the children but none of the dogs and cats in the house acquire language.
As children, we learn to think, learn to communicate and intuitively pick up an understanding of grammar rules in our mother tongue,
or native language. From then on, we learn all new languages in
relation to the one we first knew—the one that we used to understand the
world around us for the first time ever.
Although language is something we learn, research has shown that the instinct to do so is present from birth.
Not only are we inclined to process and adopt language, but it seems
that the human brain has common linguistic constraints, regardless of
the language we've learned. Certain syllables, which aren't common in
any language, are difficult for the brain to process, even in newborns who haven't started learning any language yet.
Learning a Foreign Language

When it comes to learning a second language, adults are at a disadvantage. As we age, our brain's plasticity
(its ability to create new neurons and synapses) is reduced. Following
brain damage that causes a loss of speech, for instance, researchers
have observed that children are more likely to regain the power of speech, by creating new pathways in the brain to replace the damaged ones.
One
theory of why learning a foreign language is so hard for adults focuses
more on the process we go through to do so, rather than the loss of
plasticity. Robert Bley-Vroman explains in Linguistic Perspectives on Second Language Acquisition
that adults approach learning a new language with an adult
problem-solving process, rather than in the same way a child develops
language for the first time.
Although
this means adults generally progress through the early stages of
learning a language faster than children, people who are exposed to a
foreign language first during childhood usually achieve a higher proficiency than those who start out as adults.
There's still hope, though. A study
of secondary language pronunciation found that some learners who
started as adults scored as well as native speakers. It's also been
shown that motivation to learn can improve proficiency, so if you really want to learn a language, it's not necessarily too late.
Give Yourself the Best Chance

If you want to put in the effort to learn a new language, try these methods that are known for improving learning and memory.
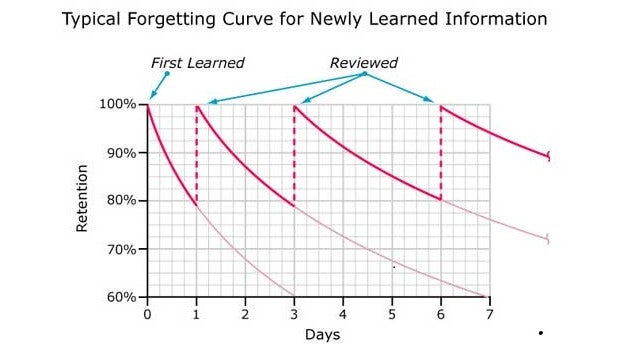
Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition is a proven memory technique
that helps you keep what you've learned strong in your mind. The way it
works is you review each word or phrase you've learned in spaced
intervals. Initially the intervals will be smaller: you might review a
new word a few times in one practice session, and then again the next
day. Once you know it well you'll be able to leave days or weeks between revisiting without forgetting it.
Here's a diagram that shows how the "forgetting curve" drops less dramatically with each new repetition:
I like using Duolingo
for vocabulary and phrase practice because it takes care of spaced
repetition for me. The app keeps track of which words I haven't
practiced for a while and reminds me to strengthen my understanding of
those. During each lesson, it mixes up familiar and new words to space
out the repetition.
Learn Before You Sleep
One of the many benefits we get from sleep is that it helps to clear out the brain's "inbox" – the temporary storage of new information and memories from our time awake. We need sleep (even just a nap)
to move anything we've recently learned into our brain's long term
storage. Once it's safely stored, spaced repetition will help to
strengthen the connection so we can recall the information faster and
more accurately.
Study Content, Not the Language
Although
most language learning classes and progams focus on purely learning the
language, a study of high school students studying French found that
when they studied another subject taught in French instead of a class
purely to teach French, the students tested better for listening
and were more motivated to learn. Students in the standard French class
scored better on reading and writing tests, so both methods clearly
have merit.
Once
you've mastered the basics of a new language, try including some
content on a topic you're interested in to improve your understanding.
You could have conversations with friends learning the same language,
read articles online or listen to a podcast to test your comprehension.
Practice a Little Everyday
If
you're busy, you might be tempted to put off your studying and cram in a
big chunk of learning once every week or two. However, studying a
little every day is actually more effective. Because your brain's
"inbox" has limited space and only sleep can clear it out, you'll hit the limit of how much you can take in pretty quickly if you study for hours at a time.
Studying in small chunks every day combines spaced repetition with the best use of the brain's temporary storage.
Mix New and Old
The brain craves novelty but attempting to learn lots of new words or phrases at once can be overwhelming. Novel concepts work best when they're mixed in with familiar information.
When
you add new words to your vocabulary, try spacing them in-between words
you're already familiar with so they'll stand out—your brain will latch
onto them more easily.










0 comments:
Post a Comment